Introducing Chonkus: The Mutant Cyanobacteria with Potential to Combat Climate Change
Stand back, ordinary ocean-dwelling, oxygen-spewing organisms: There’s a new green, hulkish mutant in town.
And hefty UTEX 3222 — dubbed “Chonkus” by the researchers who found it — may have just the right combination of traits to help with some of humanity’s most pressing problems. In particular, Chonkus could help fight climate change, report microbiologist Max Schubert, formerly of the Wyss Institute at Harvard and now launching a start-up, and colleagues in a study published October 29 in Applied and Environmental Microbiology.
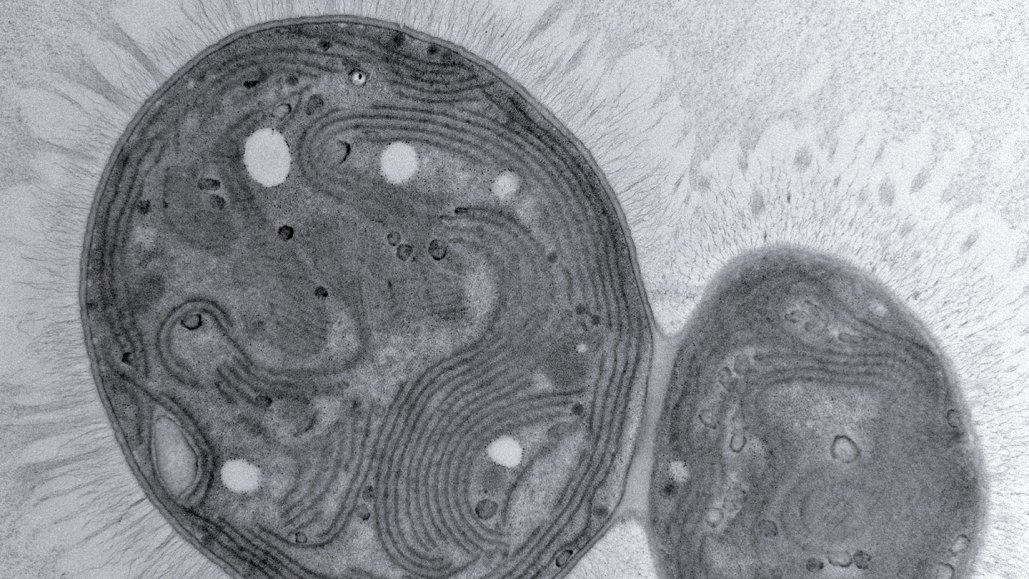
Chonkus was discovered in the shallow sunlit waters off the coast of Italy’s Vulcano Island, where volcanic gas-rich groundwater seeps into the sea. It’s an environment that Schubert and colleagues suspected to be fertile ground for finding photosynthesizing, carbon-consuming microbes. The waters collected from those seeps turned out to contain a spontaneous mutant strain of Synechococcus elongatus, a species of photosynthesizing bacteria that’s at the base of ocean food webs around the world.
S. elongatus is a favorite lab organism, because of how quickly it grows and how resistant it is to environmental stressors. And Chonkus, the new mutant, is like a superpowered version, the team found. When they cultured the strain in the laboratory, its individual cells were larger than those of other fast-growing cyanobacteria, and it built larger colonies. The mutant also contained more carbon than other strains of S. elongatus, apparently stored in white granules within its cells. The strain was also heavy: When placed into a test tube, the cyanobacteria rapidly sank to the bottom, forming a dense sludge.
Science News is collecting reader questions about how to navigate our planet's changing climate.
What do you want to know about extreme heat and how it can lead to extreme weather events?
Those traits could make Chonkus particularly effective at carbon sequestration in the ocean, the researchers suggest. Not only might it have the capacity to absorb a lot more carbon than the average cyanobacteria floating in the ocean, but it also sinks rapidly, which means it could also sequester that carbon away from the atmosphere quickly.
Chonkus’ discovery suggests that carbon dioxide-rich seeps into ocean waters may contain other rare and useful organisms, potentially including other organisms that could aid in marine carbon dioxide removal, the researchers say. And when it comes to forestalling the worst effects of climate change, such organisms may not be the heroes we deserve — but they might just be the heroes we need.
Questions or comments on this article? E-mail us at [email protected] | Reprints FAQ
M.G. Schubert et al. Cyanobacteria newly isolated from marine volcanic seeps display rapid sinking and robust, high-density growth. Applied and Environmental Microbiology. Published online October 29, 2024. doi: 10.1128/aem.00841-24.
Carolyn Gramling is the earth & climate writer. She has bachelor’s degrees in geology and European history and a Ph.D. in marine geochemistry from MIT and the Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution.
We are at a critical time and supporting climate journalism is more important than ever. Science News and our parent organization, the Society for Science, need your help to strengthen environmental literacy and ensure that our response to climate change is informed by science.
Please




