Saturday's Latest: Discoveries in Mars Limnology, Groundbreaking Phage Immunology, and Exciting Advances in Quantum Technology. Also, Get Ready for the Mushroom Invasion
The report from October 28, 2023.
This piece has undergone a thorough review in accordance with Science X's editorial guidelines and policies. The editors focused on the credibility of the content, ensuring that it was fact-checked, referenced a trusted source, and sufficiently proofread.
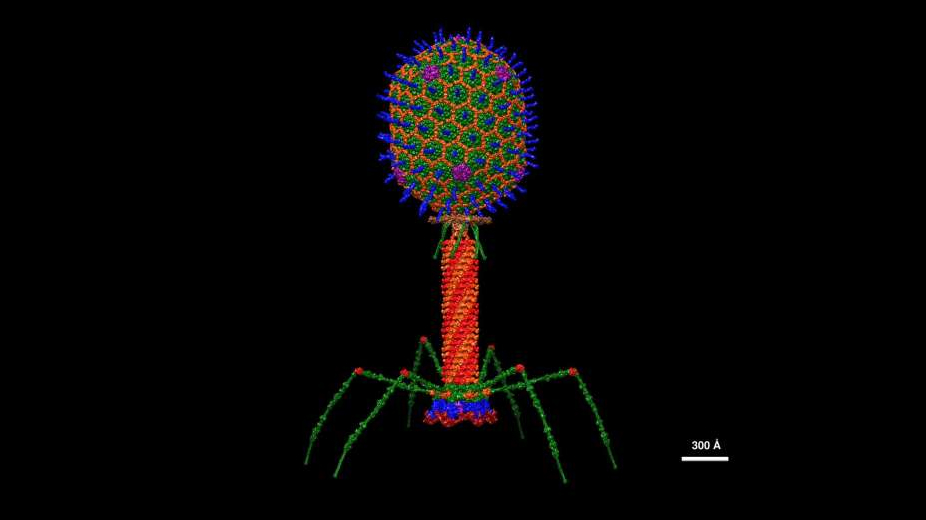
The authors of the report, among them Chris Packham from Phys.org, shared several intriguing findings this week. Included were updates on LIGO technology, parasitic fungi research, and a fresh look at Curiosity rover data. Interestingly enough, it appears that viruses do not just harm multi-celled organisms; bacteria can also fall victim to them. The process, however, resembles the terrifying scenario of the xenomorph encounter in "Alien" more than it does the common flu.
The quantum limitation seems less constraining for the Laser Interferometer Gravitational-Wave Observatory (LIGO) today. Physicists have started utilizing a quantum occurrence known as 'squeezing,' which enables them to measure gravitational waves across the full range of frequencies the observatory detects. They predict this enhancement will lead to a 60% rise in detected mergers of black holes and neutron stars.
To clarify, 'squeezing' refers to the possibility of manipulating light to enhance precision in certain aspects whilst degrading precision in others. The updated LIGO technology, which implements this principle, started operation in May 2023.
The apocalyptic PlayStation game, "The Last of Us," has made its way into the world of HBO series. The game, which features a disastrous parasitic fungi outbreak turning humans into mushroom monsters, remains the go-to reference in any fungi-related discourse. The real-world threat of airborne fungal spores and their role in a post-apocalyptic scenario are yet to be explored deeply.
Mycolgists recently discovered an interesting fact about bonnet mushrooms: they can invade the roots of living plants. There is also evidence pointing to the conversion of these Mycena fungi into mutualists, organisms that share a symbiotic relationship of mutual benefit with the host plants.
Current-day Mars does not seem conducive to life. It lacks atmospheric pressure, possesses freezing temperatures, and has no protective barrier against space radiation. However, Mars may have been different in the past. New data from the Curiosity rover suggests that Mars was once a land of rivers, raising curiosity around the possibility of ancient life on Mars.
Bacteriophages, viruses that attack bacteria, have been under scrutiny recently. A study led by Jeremy J. Barr of Monash University explores the impact of these viruses on mammalian cell immune responses. The bacterium E. coli has been shown to multiply almost instantly when attacked by the bacteriophage T4, drawing parallels with the circle of life described by Elton John.
The researchers found that when exposed to T4, mammalian cells do not activate DNA-mediated inflammatory pathways, but instead trigger signaling pathway events that promote cellular growth and survival. They say that this insight into the potentially beneficial interactions between phages and mammalian cells could contribute to the use of phage therapy for antibiotic-resistant infections.
© 2023 Science X Network




