Can holographic quantum gravity models account for cosmic acceleration?
June 22, 2023 feature
This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies. Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
- fact-checked
- peer-reviewed publication
- trusted source
- proofread
by Ingrid Fadelli , Phys.org
Theoretical physicists have been striving to develop a comprehensive theory of gravity that can account for quantum mechanics phenomena, which current models cannot. Such a theory could collectively explain the many intricate physical and cosmological phenomena observed over the past decades.
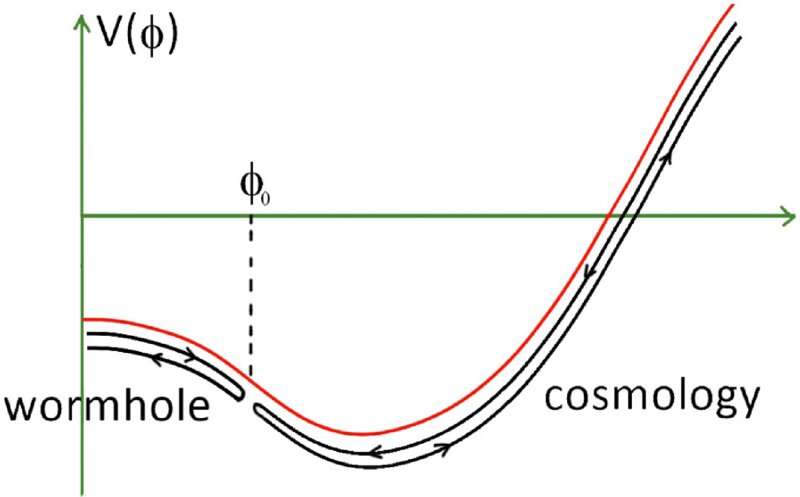
Researchers at the University of Maryland and the University of British Columbia recently conducted a theoretical study exploring the possibility that holography, which includes some features of conventional holograms, could be used to describe quantum mechanical phenomena. Their paper, published in Physical Review Letters, introduces a theoretical argument that suggests a link between observable cosmological phenomena and the physics that would underpin wormhole spacetimes.
'Coming up with a theory of gravity that includes the physics of quantum mechanics has been a major forefront area in theoretical physics for decades,' said Mark Van Raamsdonk, one of the researchers who conducted the study, in an interview with Phys.org. 'This is necessary to really understand the physics of black holes and the Big Bang, and to make progress towards a fully unified theory of physics.
'We now have fully consistent models of quantum gravity via an approach called holography, where the gravitational physics is encoded in a simpler, lower dimensional non-gravitational quantum system. Holographic gravity theories have taught us a lot about the physics of black holes and even about the fundamental nature of spacetime, but so far, there hasn't been much progress in understanding realistic cosmological spacetimes with a Big Bang.'
The key objective of the recent work by Van Raamsdonk and his colleagues was to describe the physics of cosmological spacetimes using a holographic approach. Spacetimes comprise the combination of the three dimensions of space and the one dimension of time into a single four-dimensional manifold, which underpins phenomena such as the Big Bang and cosmic expansions.
'We argue that these models can also explain the fact that the expansion of our universe is accelerating, but in a different way that what's usually assumed,' Van Raamsdonk said. 'The most conventional explanation, in what's called the Lambda-CDM (cold dark matter) model, is that we have a positive 'cosmological constant,' a type of dark energy that always has the same density throughout the universe. We argued that the holographic models can also naturally explain cosmic acceleration, but they do it via a dark energy whose density changes with time.'
Holographic models suggest that at some point the density of dark energy decreases below zero, reaching a negative value. This could, in turn, cause a deceleration and the eventual re-collapse of the universe, which is sometimes referred to as a 'big crunch.' Van Raamsdonk and his colleagues thus propose that these models may offer a different perspective on cosmological acceleration.
'We observed that quantum gravity models arising from holography can naturally explain cosmological acceleration in a novel way, with changing dark energy that eventually becomes negative,' Van Raamsdonk said. 'We don't know for sure if our universe works this way, but it's something that we can look for in cosmological observations.'
The recent work by this team of researchers offers a new perspective that could contribute to the theoretical understanding of cosmological problems that remain unresolved. Van Raamsdonk and his colleagues have already conducted further research comparing their predictions with available cosmological observations.
'We have compared the predictions of our class of model (the decreasing dark energy) with what we see from direct observations of the expansion of the universe, to see whether these seem consistent,' Van Raamsdonk added. 'With my student Chris Waddell, we looked at the most recent redshift vs. brightness data for type IA supernovae. These observations can tell us quantitatively what the expansion of the universe looked like over the past six or seven billion years. While the data don't definitively tell us whether or not the dark energy is decreasing, we found that most of the models that fit the data acceptably do have decreasing dark energy at present.'
In their next studies, the researchers would also like to better understand what the class of models they devised would predict regarding the physics of the cosmic microwave background and the distribution of galaxies in the universe. This would then allow them to compare these predictions to recent observations.
More information: Stefano Antonini et al, Accelerating Cosmology from a Holographic Wormhole, Physical Review Letters (2023). DOI: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.130.221601
Journal information: Physical Review Letters
© 2023 Science X Network




